Java PriorityQueue 源码分析
日期: 2020-04-14 分类: 跨站数据测试 480次阅读
1、概念
- PriorityQueue 一个基于优先级的无界优先级队列。
- 优先级队列的元素按照其自然顺序进行排序,或者根据构造队列时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于所使用的构造方法。
- 该队列不允许使用 null 元素也不允许插入不可比较的对象(没有实现Comparable接口的对象)。
- PriorityQueue 队列的头指排序规则最小的元素。如果多个元素都是最小值则随机选一个。
- PriorityQueue 是一个无界队列,但是初始的容量(实际是一个Object[]),随着不断向优先级队列添加元素,其容量会自动扩容,无需指定容量增加策略的细节。
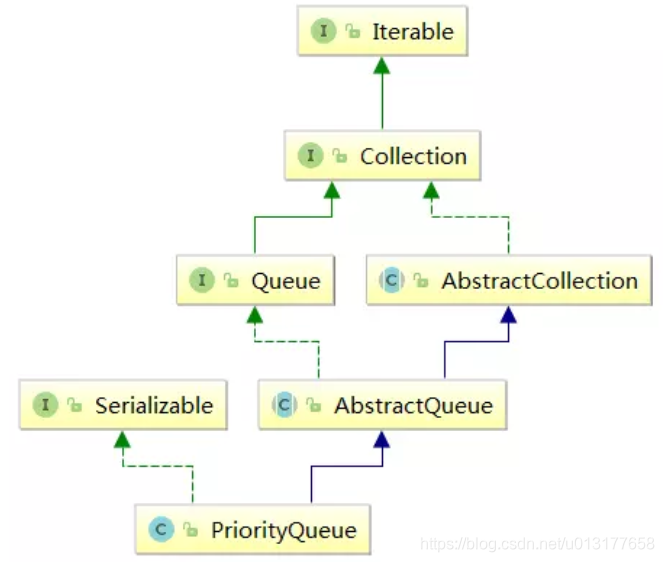
2、基本使用
PriorityQueue使用跟普通队列一样,唯一区别是PriorityQueue会根据排序规则决定谁在队头,谁在队尾。
public class PriorityQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<String> q = new PriorityQueue<>();
q.offer("1");
q.offer("2");
q.offer("8");
q.offer("6");
q.offer("5");
System.out.println(q.poll());
System.out.println(q.poll());
System.out.println(q.poll());
System.out.println(q.poll());
System.out.println(q.poll());
}
}
观察打印结果, 入列:12865, 出列是12568, 也是说出列时做了相关判断,将最小的值返回。默认情况下PriorityQueue使用自然排序法,最小元素先出列。
public class PriorityQueueTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PriorityQueue<Student> qs = new PriorityQueue<>();
qs.offer(new Student("zihao", 18));
qs.offer(new Student("haha", 9));
qs.offer(new Student("jiang", 21));
System.out.println(qs.poll());
System.out.println(qs.poll());
System.out.println(qs.poll());
}
}
class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int score;
public Student(String name, int score) {
this.name = name;
this.score = score;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getScore() {
return score;
}
public void setScore(int score) {
this.score = score;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", score=" + score +
'}';
}
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
return this.score - o.getScore();
}
}
Student{name='haha', score=9}
Student{name='zihao', score=18}
Student{name='jiang', score=21}
PriorityQueue优先级规则可以由我们根据具体需求而定制, 方式有2种:
- 添加元素自身实现了Comparable接口,确保元素是可排序的对象
- 如果添加元素没有实现Comparable接口,可以在创建PriorityQueue队列时直接指定比较器。
3、源码解析
除特别声明,本站所有文章均为原创,如需转载请以超级链接形式注明出处:SmartCat's Blog
标签:Java集合
精华推荐

